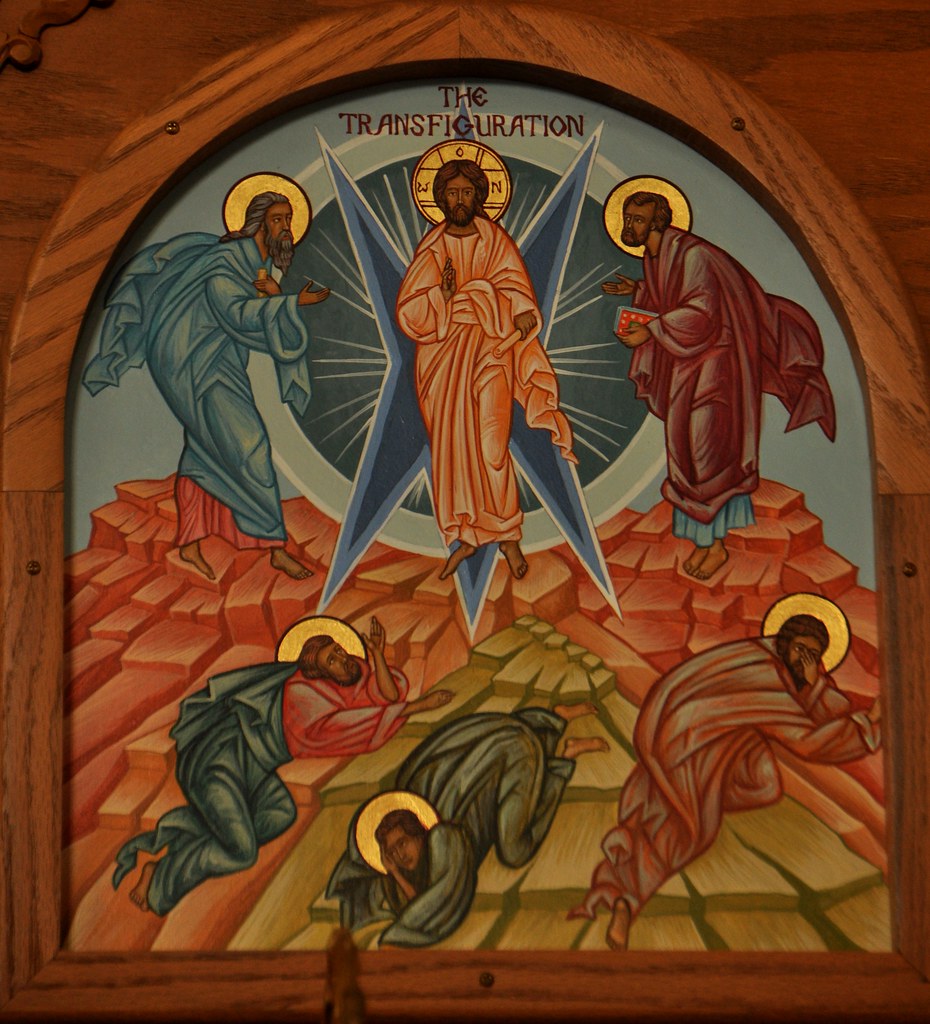
This question engages Scripture scholars and casual gospel readers alike. The Transfiguration is easy enough to describe: Jesus the teacher and miracle worker is suddenly and visibly changed on a mountaintop. He is revealed to his three closest disciples as a heavenly-connected personality claimed by a celestial voice as the Beloved Son. Jewish scholars also note that the other two heavenly beings appearing with Jesus—Moses and Elijah—shared with Jesus special roles in the age to come because of their unique end-of-life celestial "translations". This event seems more like the metamorphoses of gods familiar to Greco-Roman mythology than the Jewish tradition, however. So what's it doing in the New Testament?
First thing to note: Gospel Greek deliberately avoids the term metamorphosis in this account, an attempt to sever any "pagan"
comparison. The brilliance of Jesus' face recalls the radiance of Moses after his mountaintop communication with the Divine. The enveloping cloud also echoes the Sinai experience, and Peter's suggestion of booths or tents evokes the Tent of Meeting where Moses later encountered the Holy Presence. The simultaneous appearance of Moses and Elijah, representatives of Law and Prophecy, serve as firm anchors to the Hebrew story. No reference outside the tradition is intended or necessary.
But what are we to take away from this event? Scholars offer three possibilities. One is that this event, first noted in Mark and later retold in Matthew and Luke, is Mark's misplaced resurrection story. Early versions of Mark did not include the resurrection narrative, so this story might have been intended to foreshadow the hope of Easter. The second idea is that this story is a theological reflection of the first-generation church: a symbolic way of reconstructing what Jesus meant to them—and to us. He is the New Moses, the ultimate Prophet, the Teacher-Messiah anticipated by both Moses and the prophets.
The third theory is that the Transfiguration is a private vision Peter had—perhaps on the feast of Tabernacles or Booths while reading the appropriate Scriptures—in which the truth about Jesus "came together" for him, before or even well after Easter. Both the gospels and the Second Letter of Peter suggest that Peter had a special understanding of this event that carried with him into anticipation of the Second Coming of Jesus. Saint Paul goes further to declare that we will ALL be transfigured if we keep our sights trained on Christ.
Scripture: Mk 9:1-13; Matt 17:1-13; Lk 9:28-36;Deut. 18:15; Exod. 24:15-16; 34: 29, 35; Lev. 23:42; 2 Kgs 2:11; 2 Cor 3:18; 2 Pet. 1:16-18; see also Jn 12:28-30
Books: Rooted in Detachment: Living the Transfiguration - Kenneth Stevenson (Collegeville, MN: Liturgical Press, 2007)
Seeing the Word: The Transfiguration (The Saint John's Bible series) - (Collegeville, MN: Liturgical Press, 2010)
Reprinted with permission from PrepareTheWord.com. ©TrueQuest Communications.
More questions...and responses
- Who are the Twelve?
- What is meant by "just war"?
- What does it mean to repent?
- Is Epiphany about giving gifts or getting them?
- What's an evangelist? How many are there?
- How should we prepare for holy communion? Is fasting still necessary?
- Why are Catholics so focused on the Eucharist?
- What difference does it make that the current Pope is a Jesuit?
- What is grace?
- What is a kiss of peace?
- Can women religious work in law enforcement or in forensic labs?
- Why is being rooted in Peter's authority so important to the Catholic Church?
- My mom asked me to promise her a Christian burial. What does that involve?
- What's the vocation of a religious brother about?
- Are Hebrews the same as Jews?
- What does it mean to be saved?
- Who invented the sacraments?
- The Bible mentions Zion a lot. Where or what is Zion?
- Are halos biblical, or just an artist's idea?
- Do Catholics believe in fate?
- What am I to understand from the term "Kingdom of God"?
- Why don't all Christians celebrate Christmas on the same day?
- What do theologians do all day?
- How did the Catholic church get into the hospital business?
- Where did the breviary come from?
- What's a tertiary?
- What is heaven?
- Who are the church fathers?
- How are we to understand Jesus as both divine and human?
- Why does the Catholic church place so much importance on sacraments?
- Our pastor uses incense—a lot. Are there reasons for this?
- What are sacramentals?
- What are the marks of the church and why are they important to know?
- I'm not at peace. Is there a Catholic way to get there?
- What's a synod and why are we having one in Rome now?
- How many feast days does Mary have?
- I noticed the name "Yahweh" was taken out of a hymn I like. What's up with that?
- Why do some feasts, formerly celebrated on the church calendar, later get suppressed?
- I'm confused about "James" in the New Testament. How many are there, and who are they?
- Where did the "Hail Mary" prayer come from?
- As a Catholic, what do I need to know about racism?
- Where did the Stabat Mater come from?
- Why is Jesus called the Lamb of God?
- Please sort out these words for me: catechesis, catechetics, catechism, catechumen. What's the difference?
- What's the purpose of a wake service?
- Can a priest run for public office?
- How many church councils were there, besides Vatican I and II?
- What are the Last Rites?
- What's the significance of the Dead Sea Scrolls? I want to know—but not enough to read them!
- What are we to believe about "the Fall" in Genesis?
- The New Testament doesn't mention seven gifts of the Holy Spirit. So why was I taught about them at Confirmation?
- If you do something you didn't know is wrong, or break a church rule you didn't know exists, is it a sin?
- The Bible prohibits images, but Catholic churches are full of them. Explain?
- What does it mean to have faith?
- What are the different forms of prayer?
- As Pontius Pilate says: what is truth?
- Is it true that receiving the vaccine for COVID-19 is a sin because of how it is made?
- Do Catholics believe in faith healing?
- I thought scrupulosity was a good thing. My confessor tells me it’s not.
- Is Taizé a Catholic prayer practice and if not, what are its origins?
- We hear so much about what men do in the Bible. Do women do more than participate in the “begats”?
- Where did the idea of a Pre-Cana program come from?
- Why do Catholics light so many candles?
- Exactly how is the Pope, a human being, infallible?
- In this era of fake news, is it a sin to share juicy but unsubstantiated reports?
- How should Catholics decide how to vote?
- Why is Christianity so negative about the human body?
- What kind of authority does the church really have?
- You always hear about Vatican II. What happened at Vatican I?
- What do you have to do to get kicked out of the church?
- Have you, personally, been back to Mass yet? And if so, what was it like?
- My sister’s parish has been completely reopened for a month now, but my pastor has yet to open ours for Mass. Why is he refusing to serve us?
- How will church re-openings be handled as restrictions due to COVID-19 are relaxed?
- Will the church be different after a time of global crisis?
- Why would a global pandemic happen? Is God doing this?
- What should we do if we can't go to Mass?
- Shouldn’t churches stay open in times of crisis?
- What is temperance and do we still need it?
- When we give a blessing, what do we actually do?
- Does the church teach pacifism?
- If Jesus is God, isn’t his humanity a form of play-acting?
- Who are the Fourteen Holy Helpers?
- Are parishes necessary?
- Isn’t it a sin to vow something for life to God and then break it? Don’t fully professed sisters sin if they leave their order?
- How can I prove the existence of God to atheists?
- When will there be saints of color the U.S. can claim as their own?
- How many times has Mary appeared in history and where?
- Who or what is the Holy Spirit?
- Is Jesus the Messiah?
- What exactly is the Easter duty?
- What are beatitudes, and why are they so important?
- How does the church determine who’s “Great” and who’s a regular saint?
- Whoever came up with a feast called “Our Lord Jesus Christ, King of the Universe” to end the church year?
- What are small church communities? Are they the same as base communities?
- I keep hearing we’re all supposed to be saints. Is that realistic?
- Has Pope Francis changed church teaching on birth control?
- After we die, we “see God face to face.” Then what?
- Is Pope Francis doing anything about the sexual abuse crisis and the bishops’ woeful response?
- How can I find God in my life?
- What is prayer?
- If I attend a wedding with a full Mass on Saturday at 1 p.m., does that Mass count for Sunday?
- What’s the difference between a psalm and a canticle?
- Is it appropriate to speak of “lay ministries”?
- I’m a Eucharistic minister, and was corrected for saying cup instead of chalice. Why does it matter what you call it?
- What is the Catholic teaching regarding marriage? Does it say a marriage must be between a baptized man and a baptized woman?
- What are the “four last things”?
- What is canon law and why do we have it?
- Do I have to take a saint’s name at my Confirmation?
- Where does the Catholic teaching on abortion come from?
- Who decided we should have holy days of obligation and what they should be?
- What do Catholics believe about demons?
- Why do we have Knights of Columbus?
- Why do older folks keep quoting the Baltimore Catechism?
- Why is Easter Season so long?
- What do I need to know about Mary?
- What is spirituality?
- What do Catholics believe about the Eucharist?
- What does it take to be recognized by the church as a saint?
- Two Americans were beatified by Pope Francis. What do I need to know about them?
- What’s the purpose of Ordinary Time?
- The church made Mother Teresa a saint overnight. Why is it taking so long for Bishop Oscar Romero?
- What does the phrase “consubstantial with the Father” in the Creed mean?
- What does Pope Francis mean by “rapidification”?
- I'm having trouble finding a religious community that will consider me as a candidate because I'm older. Why?
- I don’t read papal documents. What do I need to know about Laudato Si?
- Is God a name, like Allah or Jesus?
- Why should I go to church?
- What is the common good?
- Why is prejudice against Catholics called “the deepest bias in the history of the American people”?
- Why does going to Mass on Saturday night “count” to fulfill the Sunday obligation?
- Don’t we have to obey what the church teaches, or be kicked out?
- How do I reconcile patriotism and faith? Sometimes it feels like dueling citizenships!
- Our priest cancelled Saturday Vigil Mass, citing Dies Domini and pastoral necessity. Is this valid?
- With the recent opposition to Muslim immigrants, I wonder: Were Catholics always welcomed here?
- Is Pope Francis the first Catholic leader to address the environment?
- Do all Christians basically agree on the purpose of baptism, Eucharist, and ministry?
- What is natural law?
- Some of my friends view belief in God as anti-intellectual.
- How did the veneration of relics get started?
- Why do we worship in buildings instead of in God’s beautiful creation?
- What are Catholics to believe about the Antichrist?
- How can I understand and explain the Catholic position on contraception?
- How is it determined that someone is a saint?
- What can we expect from the Vatican Commission on women deacons?
- Who were the women at the cross?
- Is the Bible infallible?
- Can Catholics practice yoga?
- Where can Mass be celebrated?
- I've been told Catholic devotion to saints contradicts what the Bible says about graven images.
- Where in the Bible does it say Jesus' birthday is December 25th?
- Is Jesus truly the Son of God or is it just a story?
- If you're married, is it still possible to become a priest? If yes, what are the steps needed?
- What's a halo, really?
- Why do Catholics put so much emphasis on Mary and the saints?
- Is the parish expected to give the pastor and secretary a bonus at Christmas?
- I recently became a Freemason but feel a calling to be a priest. Do I have a canonical impediment?
- Is it necessary to attend Mass on Sunday? I can't go to church because of my job. What should I do?
- Can Catholics be cremated?
- Is it a sin to eat meat on Fridays during Lent or just a suggestion?
- What exactly is a "Jubilee Year"? What's a "Holy Year"? I hear the Year of Mercy called both.
- Is astrology compatible with Christian belief?
- What does Advent have to do with Apocalypse?
- Petra is the coolest historical site in Jordan. Is it biblically significant?
- Where is Moses buried?
- Settle an argument for me. Was Jesus baptized in Jordan?
- Is the clerical sexual abuse crisis over?
- Who is Karl Rahner, and why is he important?
- Is there a protocol for paying the priest: for marriages, sick calls, last rites?
- Are priests obliged to say mass every day?
- I heard all the big heresies were invented by the 5th century
- What does the church have to say about suicide?
- Where did Limbo come from?
- Mary's parents aren't mentioned in the Bible. How do we know their names?
- Was there ever such a thing as a deaconness?
- Who was Origen?
- How do you know if you're committing heresy?
- Do Catholics believe in psychology?
- Is there a heaven? What is it like?
- What's important about the Avignon papacy and the Great Schism?
- What do I need to know about the Crusades?
- What's an abbess, and what power does she wield?
- Is premarital sex a sin?
- Do the Eastern churches have popes?
- What is papal primacy and where does it come from?
- What does Jesus have to say about family?
- Why do we have priests?
- Why do we "respect life"?
- Why do we honor martyrs?
- What is a patron saint?
- Is there truth in other religions?
- What do Catholics believe about war and peace?
- Why do some buildings have feast days?
- How do you figure Transfiguration?
- What is the Immaculate Heart of Mary?
- What is the Sacred Heart of Jesus?
- What is humility?
- Is it possible to prove the existence of God?
- How “Roman” is the Roman Catholic Church?
- How do can you deal with sinful thoughts?
- What is virtue?
- Does God get angry?
- Why do we have a Rite of Christian Initiation of Adults?
- Why do we fast?
- What are the qualifications for being pope?
- Is it OK for Christians to be rich?
- What is the Roman Catholic view of work?
- What is Baptism?
- What do we know about Saint Joseph?
- Why is there a church calendar?
- What is the “deposit of faith”?
- What’s the purpose of incense?
- What is “mission”?
- Why is marriage a sacrament?
- Where did American Catholic schools come from?
- What is the Anointing of the Sick?
- Why do we hear scripture readings at Mass?
- What about the violence in the Old Testament?
- What’s the difference between “the gospel” and “the gospels”?
- What is the Sacrament of Confirmation?
- Why are there cults?
- What’s in a papal name?
- What is Pentecost?
- What is Christ’s Ascension?
- What are the different forms of prayer?
- What is the Real Presence of Christ?
- How can the pope resign?
- Can Catholic doctrine change in light of new information?
- Why is the Lord’s Prayer so important?
- Love thy extraterrestrial neighbor: Does the church believe there could be life on other planets?
- What do Catholics believe about the divine inspiration of scripture?
- Who was John the Baptist and what was his relationship to Jesus?
- What is the structure of the church and what do the people in it do?
- Are there other kinds of Catholics besides Roman?
- What does the "Word of God" mean?
- What are visions?
- What is Purgatory?
- What are third orders, oblates, and associates?
- Why sing at Mass?
- What about all the different gods in Hebrew scripture?
- Is there a place for dissent in the church?
- Do Catholics believe in evolution?
- What does the Bible say about God?
- Why do we say Jesus "descended into hell"?
- Why does God let bad things happen?
- Is it OK to use “real” bread at Mass?
- What is Wisdom?
- Is there a “right time” to be called by God?
- How can I understand the Holy Trinity?
- Why are there two Creeds?
- “How can I live as a Christian in the modern world?”
- Saint Thomas Aquinas did what, exactly?
- Why did American Catholicism begin in Baltimore?
- Do religious communities work for human rights?
- Why isn’t the "Gloria" sung during Lent?
- Should people in discernment date?
- Why do Catholics wear ashes on Ash Wednesday?
- Where did Lent come from?
- What’s so important about the Council of Trent?
- What are the “Precepts of the Church”?
- Do Catholics take the biblical creation story literally?
- Why can’t a woman be ordained?
- Why does the liturgy change?
- Which religious community is right for me?
- Is Purgatory still “on the books”?
- Why is it important to participate regularly in the Mass?
- Why pray the rosary?
- Why can people go to Mass on Saturday evening instead of Sunday?
- I feel called to be a sister, but I am not yet 18 years old
- Did King David compose the psalms?
- Who were Jesus' “brothers and sisters”?
- Is there really a Catholic Index of Forbidden Books?
- What can I do about my student loan debt if I want to join a community?
- What are the corporal and spiritual works of mercy?
- Is a long or short discernment process better?
- What’s the difference between celibacy and chastity?
- Is it “Catholic” to be vegetarian? Do Catholics care about animal suffering?
- What does the Bible say about Judgment Day?
- How can I talk to my parents about my vocation and get their support?
- Why do Christians believe Jesus is God incarnate?
- What’s that picture of Jesus with rays flowing from him?
- What is the Triduum?
- Can someone change religious communities?
- Who chose the "Seven Deadly Sins"?
- What should I believe about hell?
- Why are there different kinds of Franciscans?
- Is the Mass a “holy sacrifice” or a “celebration”—or both?
- Pulpit, lectern, ambo: What’s the difference?
- What was the Reformation?
- If you have a mental illness, can you still join a religious order?
- What is “discernment of spirits”?
- Why would someone want to be a priest, sister, or brother?
- Is environmentalism “Catholic” or a political football?
- Why do Catholics believe in the Immaculate Conception?
- Why are there parishes?
- Do Catholics believe in ghosts?
- Who was Saint Augustine?
- Is a college degree needed for religious life?
- What is "sanctuary"?
- What is the Liturgy of the Hours?
- How do I discern my calling to priesthood or brotherhood?
- How does God “answer” prayers?
- As a sister, would I have to give up sports?
- What does “salvation history” mean?
- Why do Catholics believe in the Assumption of Mary?
- Can I keep doing my music when I enter religious life?
- Why do priests wear vestments?
- Do miracles still happen?
- How can I find a good spiritual director?
- What do deacons do?
- How is the Mass “prayer”?
- What is Catholic decision-making?
- Can I have a job if I join a religious community?
- Who wrote the gospels?
- Can converts become sisters or brothers?
- What is “original sin”?
- How does the Catholic Church view other religions?
- The "Five C's" of Confession
- Discerning your vocation
- What's the difference between chapels, churches, cathedrals, and basilicas?
- Where do the Stations of the Cross come from?
- What's the relationship between the Old Testament and the New Testament?
- What about wearing habits and and taking "religious" names
- When and where is it appropriate to bow inside Catholic churches?
- Older vocations
- Can I come back to the church?
- Why does the priest talk after the readings at Mass?
- Is being divorced an obstacle to religious life?
- What's the difference between catechesis and evangelization?
- Didn't Saint Paul write all the letters attributed to him?
- Are we supposed to believe in angels and demons in the 21st century?
- Who are the saints and why do we pray to them?
- How does a religious community start?
- Why pray for the dead?
- Dealing with stage fright
- Who are the "Doctors of the Church"?
- How were the books of the Bible chosen?
- What's the difference between saying "set" prayers and prayers in my own words?
- Paying for seminary
- If I join a religious community do I have to change my name and cut my hair?
- What do Catholics have to believe?
- Who were the prophets? Does God still call people to prophecy?
- What is the lectionary?
- Why do Catholics bless themselves, genuflect, and so on?
- How did we get from following “the Way” of Jesus to the church?
- What do we mean by the church’s “magisterium”?
- Is there salvation outside the Catholic Church?
- What do people in religious life do for fun?
- Why is celibacy important to religious life?
- Vocation: For all of life, or only "religious life"?
- What is contemplation?
- Is my vocation from God or just my imagination?
- What does the Bible say about discipleship?
- How do I know whether be an order priest or a diocesan priest?
- What do Catholics believe about scripture and tradition?
- "Sin" is such a negative word. Can't we just talk about “failure”?
- Why should I read the Bible?
- Will my faith make me happy?
- How can I live a holy life?